Abstract
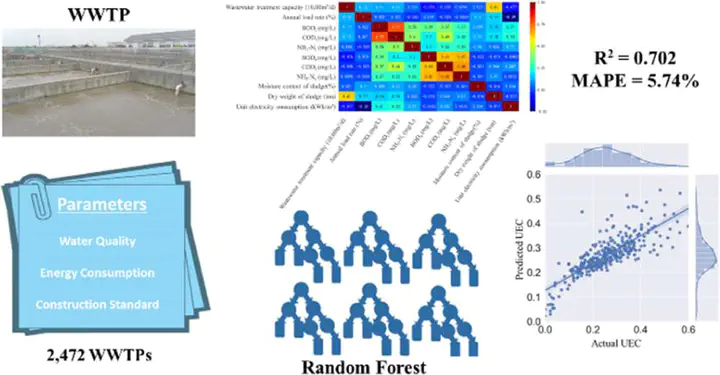
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) can account for up to 1% of a country’s energy consumption. Meanwhile, WWTPs have high energy-saving potential. To achieve this, it is necessary to establish appropriate energy consumption models for WWTPs. Several recent models have been developed using logarithmic, exponential, or linear functions. However, the behavior of WWTPs is non-linear, and difficult to fit with simple functions particularly for non-numerical variables. Thus, traditional modeling methods cannot effectively describe the relationship between water and energy in WWTPs. Therefore, a machine learning method was adopted in this study to investigate the energy consumption in WWTPs; a novel energy consumption model with a non-numerical variable (discharge standard) for WWTPs was developed using the random forest algorithm. The model can also predict the energy consumption of WWTPs after upgrading discharge standards. We found that the unit electricity consumption of WWTPs exhibited an average increase of 17% after the effluent discharge standard was raised from Class I B to Class I A (per China’s classification). The correlation coefficient of the model was 0.702, and the Mean Squared Error was 0.0112 (kWh/m3)2, while the Mean Absolute Percentage Error was 6.86%. Thus, the developed model can provide a better understanding of energy efficiency in WWTPs.