Evaluation on the efficiency of wastewater treatment plants with data envelopment analysis from a water-energy nexus perspective
Abstract
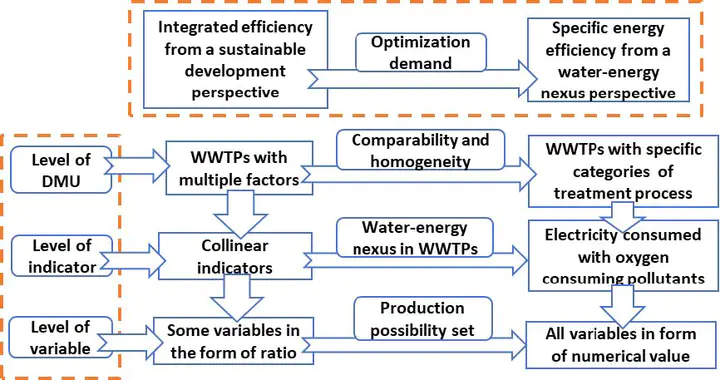
With the urgent demand on the optimization from both aspects of water quality and energy consumption, the efficiency of WWTPs from a water-energy nexus perspective appears to be increasingly important. In this study, the energy efficiency of 210 WWTPs in Yangtze River Delta of China were assessed through data envelopment analysis (DEA). The operational conditions of DEA were polished through a hierarchical framework. All WWTPs were classified into 4 categories of anaerobic-anoxic-oxic (AAO), anaerobic-oxic (AO), oxidation ditch (OD) and sequencing batch reactor (SBR). And the variables derived from the indicators were revised through production possibility set (PPS) in order to remove the ratio form. The results showed that WWTPs in Yangtze River Delta had a high efficiency overall. It also indicated that advanced treatment process didn‘t have a remarkable impact on the efficiency. Moreover, there were much room for the optimization on pollutant removal in terms of the ideal discharge limit converted from the projection.